All computers rely on batteries in them. For both laptops and desktops use a non-rechargeable Lithium coin cell to power a chip called the Real Time Clock when the computer is not switched on. Laptops also have a battery for mobile use and “Spicy Pillows” that can be the result of them deteriorating.
The IBM PC
The IBM PC and the clones of that era, including the IBM PC Jr did not have a battery nor a Real Time Clock, so users had to set the date and time every time they turned on their machine or rebooted.


Real Time Clock
The Real Time Clock is a chip on the motherboard that is powered by the power supply while the computer is powered on and by a CMOS battery (sometimes called Non Volatile) when the computer is powered off.
Early computers had the battery soldered to the motherboard and were in the form of Ni-Cd or Ni-Mh batteries. Later computers standardised and used non-rechargeable cells known as CR2032, where the cell is 20mm diameter and 3.2mm thick.
In later computers the BIOS (Basic Input Output System) was introduced to map the hardware to the operating system and provide additional functionality and the settings are stored in a battery backed RAM chip.
Modern computers use a much more updated system called UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) that dispenses with the RAM chip and stores the settings inside the SuperIO instead, this also means that a BIOS password could not be removed by removing the battery.


Laptop batteries
Early transportable laptops used Ni-Cd battery packs consisting of many battery cells joined together. Later, laptops were powered by Lithium Ion battery cells in much the same way. You can see these in laptops with user removable batteries.
Modern laptops use flat battery cells, usually located under the keyboard but on 2-in-1 laptops/tablets the battery is under the screen.
Batteries can die from overuse, and its common for users that use laptops as desktop computers by keeping them constantly connected to the charger that the battery perishes and refuses to hold its charge.


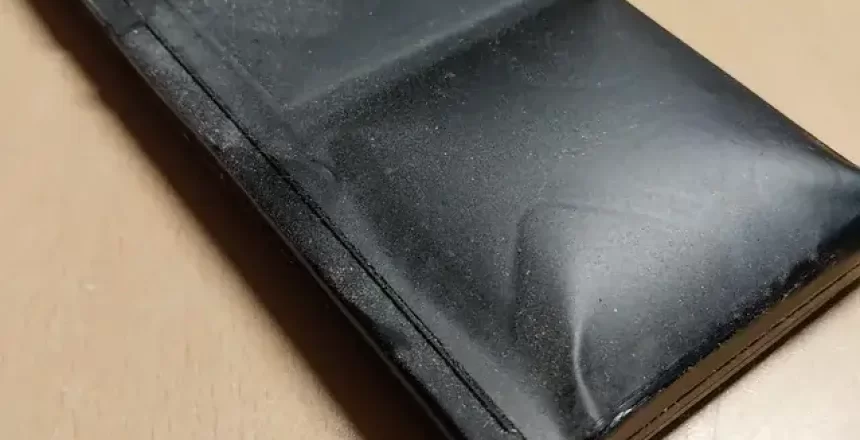
Spicy Pillows
Spicy Pillows is the tech nickname for dangerously swollen batteries that distort the shape of the device they are installed in.
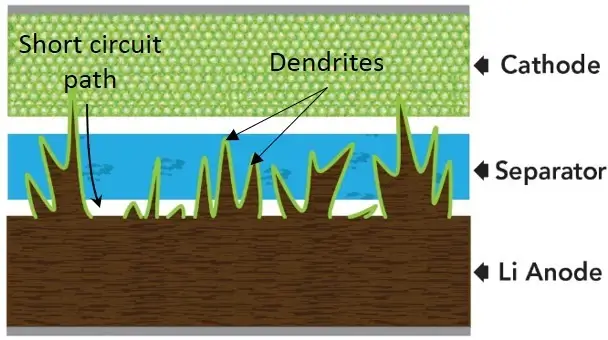
In Ni-Cd days, the battery cells grew dendrites (tiny metal spines) that grow on the anode or negative side of the cell over to the cathode or positive side of the cell and effectively shorten the lifespan of the cell, or create a dead short across the cell so the capacity of the cell is much reduced. Ni-Cd cells could be zapped with a welder to dissolve the dendrites and recover the cells.
Lithium Ion battery cells also grow dendrites from the anode, causing the cell to expand. If the dendrites get too close to the cathode, they can spark and cause the cell to explode or catch fire. Overcharging and overheating the battery will also result in an explosion or fire.
Modern batteries have a BMS (Battery Management System) that balances the cell charging and levels across the battery pack.
Conclusion
Battery replacement is inevitable, be it a laptop battery or desktop battery as nothing lasts forever. While replacing the CMOS battery in a desktop is relatively easy, replacing a laptop battery often requires an almost total disassemble.

