There are so many different things to consider when buying a new monitor. It all depends on what your intentions are.
Let’s start with the type of screen you need:
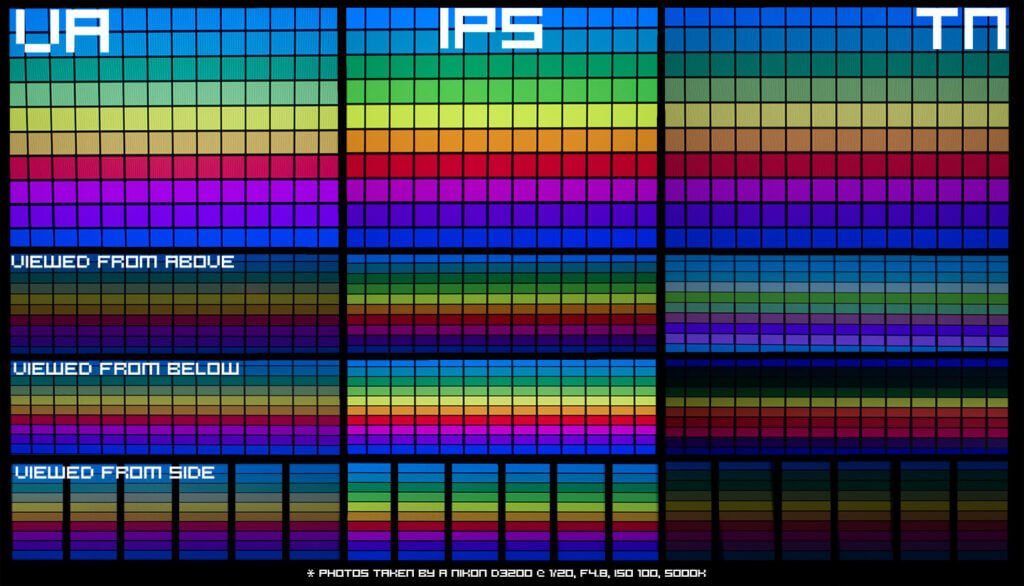
TN - Twisted Nematic
TN Panel monitors are the cheapest monitor technology available and has higher response times which makes them well suited as an all round monitor, and because of the high refresh rate, they are suitable for playing games.
The downside to TN Panel is that they have poor viewing angle, as well as poor contrast, so they don’t provide a good enough quality for video or image editing.
Prices start from around £55 for a 15.6″ to £350 for 28″ 4K monitor, though considerably more if you want a gaming monitor.
IPS - In Phase Shift Panel
An IPS Panel on the other hand has great contrast and viewing angles which makes them ideal for video and image editing.
However, they have a higher response time which may make them unsuitable for gaming.
Prices start from £80 for a 23″ to over £1,000 for a 38″ 4K monitor, although again considerably more for a gaming monitor.
VA - Vertical Alignment
VA Panel offers a hybrid between the two popular panel types, improving the refresh rate while increasing the colour contrast.
Prices start at £90 for 21.5″ HD to over £1,000 for 34″ 4K, although gaming monitor are considerably more.
PLS - Plane to Line Switching
A PLS panel is very similar to an IPS panel, but with some additional minor advantages. PLS is basically Samsung’s improved version of IPS.
Prices start from around £110 for 24″ and £330 for 27″ 2K monitor.
Monitor resolution
In the early days of flat screen monitors, they followed the aspect ratio of CRT monitors, usually 4:3 or 5:4.
However, with the introduction of HDTV and widescreen, the accepted ratio was 16:10 until 2008. After 2008, the accepted ratio changed to 16:9, which meant that screens were cheaper to manufacture.
Today, most monitors are sold in HD ratio:
- Full HD or 1920×1080
- QHD or 2K (2560×1440)
- UHD or 4K (3840 x 2160)
Additionally Apple sells monitors in 5K (5120 x 2880)
Screen size
In the past, it was common to have screen sizes of 14″, but the smallest size is now 15″ for desktop computers. The largest HD ratio screen is 34″, beyond this there are wider ratio screens offering 32:9 resolution, effectively double width screens.
Response times
Response times are about how quickly a screen can shift from one colour to another. When surfing the web; writing word processor documents and editing photos, response time is not a problem. Even when watching video, screen response time is not a problem.
However, when gaming, the monitor needs to have the lowest number, and therefore the quickest response time.
Refresh rate is different to response time.
Refresh rate
Refresh rate refers to how quickly the picture is updated. At 60Hz, the screen reloads the screen 60 times a second.
The refresh rate of the screen isn’t that noticeable in normal day-to-day activities but when gaming, the faster the screen refreshes, the more changes can be reflected and some monitors have refresh rates of 240Hz, 4 times faster than common 60Hz screens.
Touch screen
In the past, if you wanted a touch screen monitor, it meant you had a resistive screen which worked well with a stylus and roughly with finger touch.
However, with the advancement of capacitive touch screens, multi touch is now available bring many gestures to the screen like pinch and zoom.
You can buy overlays to enable a touch screen on a non-touch monitor, however upgrading a non-touch screen to a touch screen can be expensive, and its often much cheaper to buy a touch screen monitor than adapt one. The exception to this is with an all-in-one computer, where a touch screen model is considerably more expensive than a non-touch screen one.
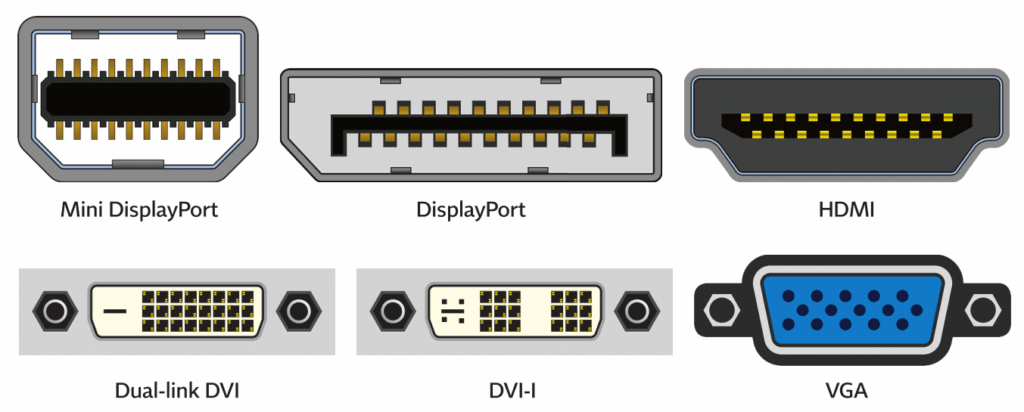
Connection types
In order to connect your monitor to your computer, you need to make sure you buy a monitor with the same connections as your computer. The connectors are:
- VGA – Video Graphics Array. VGA is an analogue standard, which means that the individual RGB (Red, Green and Blue) channels are controlled individually. Only pictures can be sent down a VGA cable, sound is provided using an analogue cable connection if the monitor has speakers. The VGA cable plug and socket are blue. VGA is often referred to as legacy, because it is the oldest of the connector types, and was most commonly found on older CRT monitors.
- DVI – Digital Video Interface. DVI is the next step up from VGA, with a connector that can do analogue or digital, depending on the graphics card. Like VGA, sound is provided with a separate cable. The DVI connector is white.
- HDMI – High Definition Multimedia Interface. HDMI provides both video and audio as a single digital connection. The connector is black.
- DisplayPort. DisplayPort works similar to HDMI, but can provide faster data transfer which allows for higher refresh rates and better quality than HDMI.
- USB-C. USB is a new technology that allows for digital video; audio; data and power to flow through a single connector.


