Most people on Fibre Broadband have fibre delivered to a box in the road and then copper to their home which is known as FTTC or Fibre to the cabinet. For people on Full Fibre, this is called FTTH or Fibre to the home or FTTP – Fibre to the premises. FTTR is a new technology.
What is FTTR?
Back in 2021, the ITU drew up technical documents for a new technology coined FFTR, or Fibre to the room. This technology involves running a tiny fibre optic cable around door frames and into rooms so that they can be coupled to small “mesh” routers in each room.
This means that each room gets a wireless transmitter that has the same name and password across the entire property. Since each room gets its own WiFi router, there are no dead zones and each router provides localised wireless at full speed.
What are the advantages?
FTTR currently operates at a maximum of 10Gbps between the main ONU to the sub ONUs which then provides 1GBps ports and WiFi in each room which is easily capable of:
- Video calls
- Video conferencing
- HD streaming (8K)
- Augmented and Virtual Reality
What is involved?
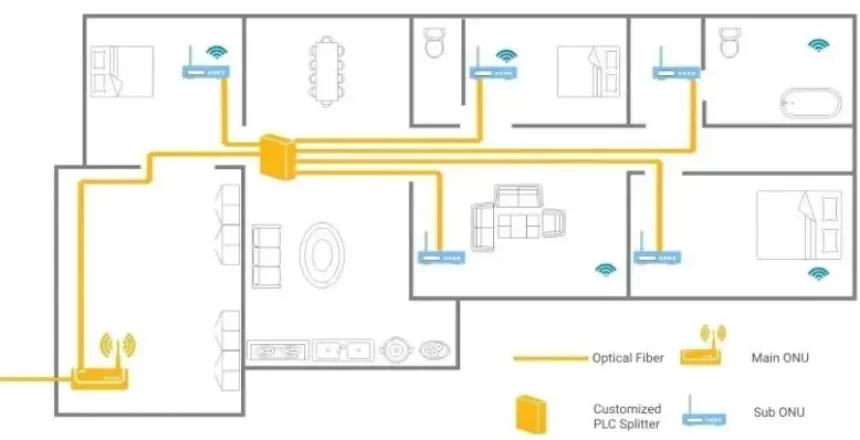
There are a number of components:
- Main Optical Network Unit (ONU) – This connects the provider’s optical fibre to the premises.
- Sub ONU – These are located in the individual rooms.
- Optical Splitter – This connects the Main ONU to the Sub ONUs.
- Fibre optic cable – This is routed round door frames between the Main and Sub ONUs.
- Wall boxes – These are used to terminate fibre optic cables that are currently not in use.