When the Internet doesn’t work, we need to find out why. If you have wireless and wired devices, such as a tablet or smart phone, see if they connect to the Internet to rule out any problem localised to the computer.
Localised problems
Check to see if the cable has disconnected itself, if you are using a wired network. You should be able to see one or two flashing lights on the back of the computer.
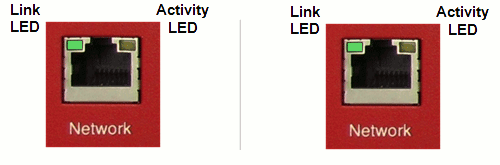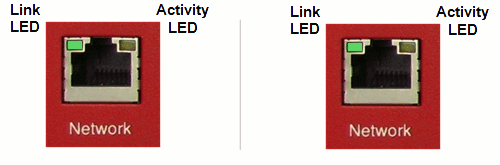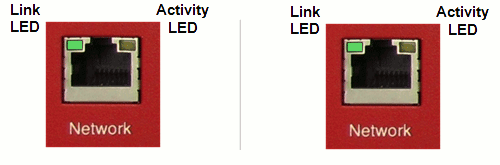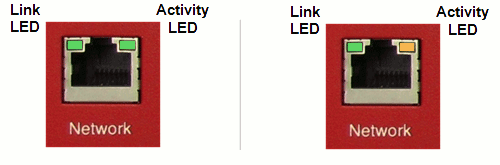
Network problems
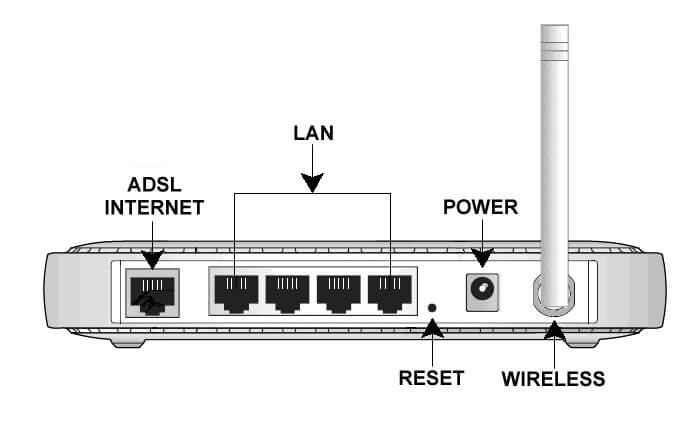
In the diagram above, you will see the connectors required on a standard wireless router. If you are having problems, start by unplugging the power connector and plug it back in to give the router a clean start before diagnosing any further problems. Sometimes, a clean start is all that is needed to resolve network issues. However, if problems persist, carry on reading.
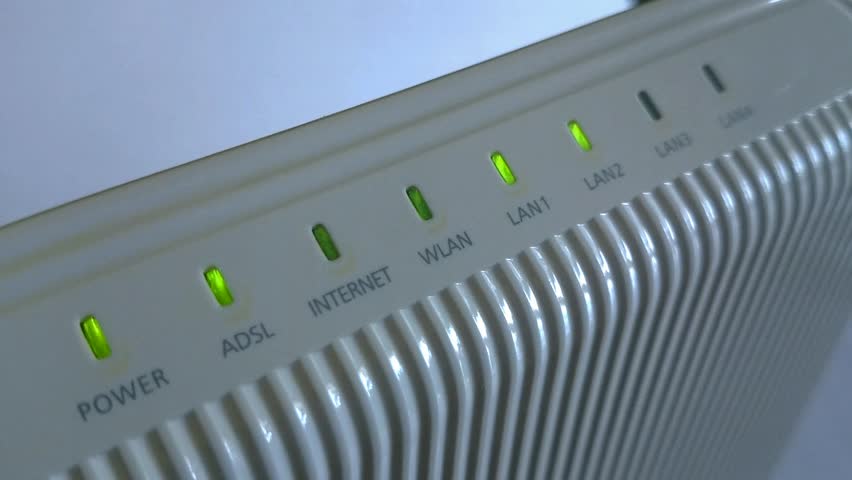

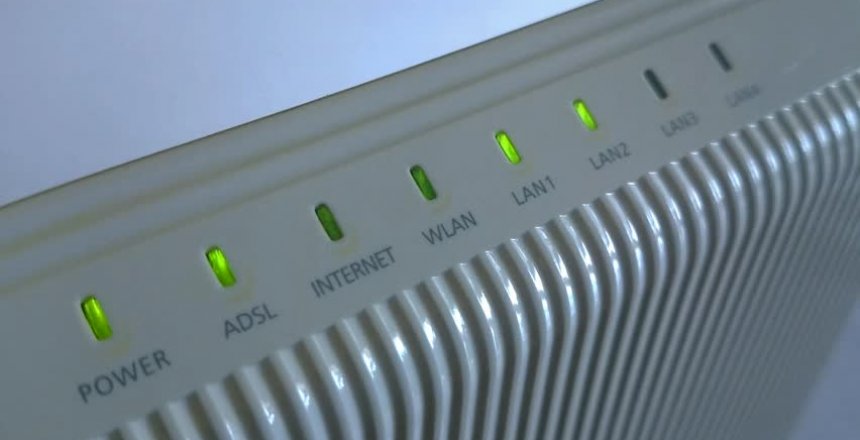
Unless you are using a BT router, you will see different lights for different purposes.
Power light
You want to make sure that the power light is on, it means the router is plugged in
ADSL (or DSL)
This shows you have a connection to the telephone line and there is a connection to the DSL equipment at the exchange. If the LED is not lit, you have a line problem or a filter problem. Make sure the cable is connected to the router and to the designated telephone socket or a filter.
Note that if you are using a master socket with a dedicated DSL socket, no other socket around the home will have the capability to provide DSL, unless a qualified telephone engineer has installed an appropriate socket for that specific purpose.
Remove the front panel of your master socket and connect a filter into the test socket, this rules out any house wiring that may be the issue. If the DSL light stays off after a few minutes, then report a line fault.
Internet
The Internet light means that the router has talked to your ISP and has exchanged the username and password assigned to your account. If it’s red or not lit, then there is an authentication problem. This either means they have changed the password; billing has failed or your ISP has a server problem.
WLAN or Wifi
This indicates that you have a wireless network provided by the router, if the light is turned off, the wireless part of the router is disabled. It flashes in operation.
LAN
LAN or Local Area Network lights show activity and connectivity for computers and other devices that are connected to the router using the wired network. Illuminated they show connections, flashing means activity and extinguished means they are not connected or the device connected is not switched on.
BT Hub status colours
Unlike other routers that show exactly what is going on in detail,BT introduced colour codes for their Hub routers. This includes the Smart Hub (known as Hub6), Home Hub 3 and above as well as the Business Hub.

Flashing purple light means the Hub is working but not connected to the Internet. This often happens if the router is being used as a Wireless range extender on a network that isn’t BT.
Solid white light means the router is in bridging mode, it means that it extends the network it is connected to and disables all other features. Often more likely used on a Business network.
BT Hub warning lights
In addition to the single colour light, there are two warning lights that may come on.
Orange b means there is no broadband detected on the line. Either you have a line fault or the broadband has not been enabled yet
Red b means there is a password problem with the router, you need to press the Reset pin with a paper clip.
Flashing red b means there is a problem with the broadband
Orange Wifi symbol means that the Wifi is switched off.
Flashing Orange Wifi symbol means that WPS has been enabled. WPS means Wifi Protected Setup and is enabled by holding down the WPS button on the Hub. It is used to connect devices such as printers where you can’t enter the Wifi passcode.


